As part of September’s Hazard of the Month, Fire, we’re highlighting two key areas: Electrical Safety and Fire Safety.
Electrical Safety
 Electricity poses a significant risk, with the potential to cause severe injury, fatalities, and extensive property damage. Even non-fatal electrical shocks can result in serious, lasting injuries. Therefore, it is crucial to implement effective safety measures and ensure that workers can identify potential electrical hazards.
Electricity poses a significant risk, with the potential to cause severe injury, fatalities, and extensive property damage. Even non-fatal electrical shocks can result in serious, lasting injuries. Therefore, it is crucial to implement effective safety measures and ensure that workers can identify potential electrical hazards.
To reduce the risks associated with electrical equipment in the workplace, consider the following actions:
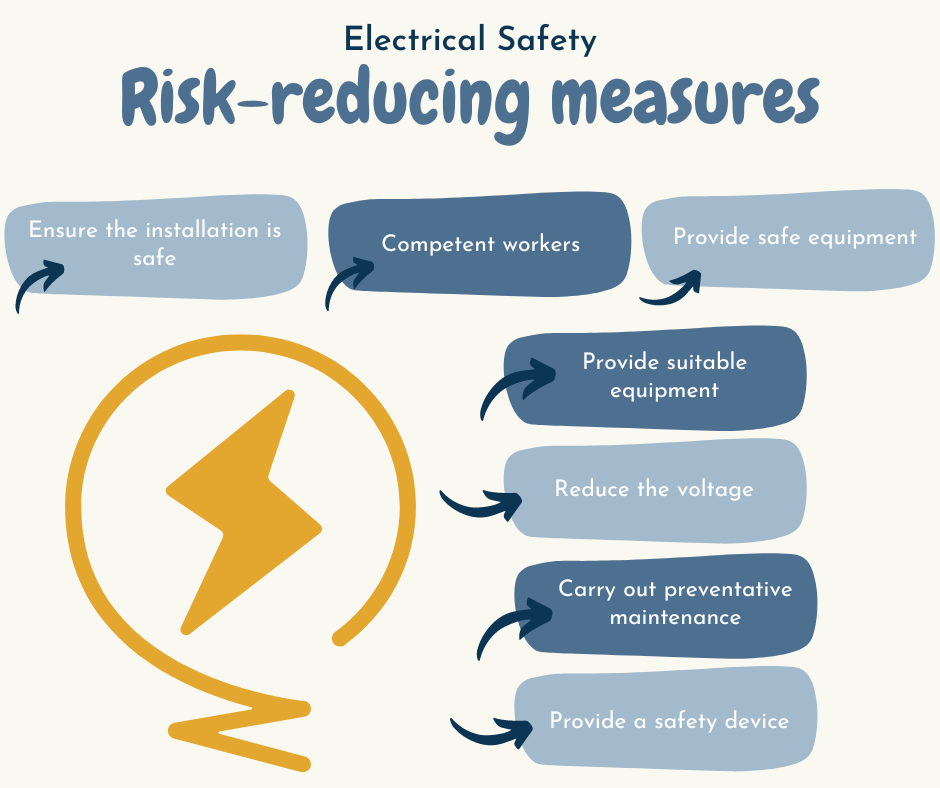
- Ensure safe installation: Ensure that new electrical systems meet appropriate standards and that existing installations are regularly maintained.
- Use competent workers: Workers handling electrical equipment must have the necessary training, skills, and knowledge for the task.
- Provide safe equipment: Equipment should be in a safe condition when supplied and consistently maintained to ensure ongoing safety.
- Supply suitable equipment: Ensure that equipment is appropriate for the specific task and working environment.
- Reduce voltage: Limit the voltage supply to the lowest level necessary to complete the job.
- Conduct preventative maintenance: Maintenance schedules and check frequencies should be determined in consultation with equipment users, based on the risk of equipment failure.
- Use safety devices: A residual current device (RCD) can provide additional protection when using equipment operating at 230 volts or higher by detecting faults and quickly shutting off the power.
While employers are responsible for ensuring the correct controls are in place, employees also play a critical role in reducing electrical risks by understanding the dangers and being aware of potential hazards.
Learn more about how to control electrical safety in the workplace with our Electrical Safety Online Training Course. Get 10% off this course with the code ‘fire10’!
Fire Safety
 Working with flammable substances such as gases, vapours, mists, or combustible dusts can result in fires or explosions if they come into contact with air and are ignited. Such incidents can cause significant harm to people, property, the environment, and businesses.
Working with flammable substances such as gases, vapours, mists, or combustible dusts can result in fires or explosions if they come into contact with air and are ignited. Such incidents can cause significant harm to people, property, the environment, and businesses.
To minimise these risks and ensure workplace safety, it is essential to implement preventative measures such as proper storage, ventilation, and employee training.
Flammable substances that can cause fires come in various forms, including:
- Liquids: Such as petrol, fuels, inks, paints, adhesives, and cleaning fluids. These liquids emit flammable vapors that can ignite or explode when mixed with air.
- Dusts: Including coal, wood, sugar, flour, grain, synthetic organic chemicals, and certain metals. These dusts may be raw materials, intermediates, finished products, or waste. They are common in industries like food production, animal feed, chemicals, woodworking, rubber and plastic processing, and metal powder production. Combustible dust clouds can cause violent explosions if ignited.
- Gases: Such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), hydrogen, and other flammable industrial gases. Typically stored in pressurized containers, uncontrolled releases of these gases can easily ignite.
- Solids: Including materials like packaging, plastic foam, and textiles. These can burn intensely and produce dense, often toxic, smoke.
Learn more about how to control fire hazards with our Fire Safety Online Training Course. Get 10% off this course with the code ‘fire10’!

Electrical Safety and Fire Safety training courses are essential tools in preventing fires in the workplace. Make sure you don’t miss out on our 10% off deal on these courses, available until the end of September. Simply enter the code ‘fire10’ at checkout to save!
Read more Safety Spotlight blogs here
To keep up to date with the latest health & safety news and advice, follow us on social media:
